Frequently Asked Questions
What is str in teaching?
The Science of Teaching Reading (STR) Exam.
What is the STR exam for teachers?
The STR exam is a set of standards created by the State Board for Educator Certification (SBEC) that addresses the discipline and practice of teaching reading to young learners.
Who has to take the STR?
All educators who teach in any grade starting from prekindergarten through the 6th grade need to take the Science of Teaching Reading exam.
Additionally, in order to receive an intern, probationary, and/or standard certificate, the following fields are required to pass the exam:
- Core Subjects with Science of Teaching Reading: Early Childhood – Grade 6
- Core Subjects with Science of Teaching Reading: Grades 4 – 8
- English Language Arts and Reading with Science of Teaching Reading: Grades 4 – 8
- English Language Arts and Reading/Social Studies with Science of Teaching Reading: Grades 4 – 8
- Early Childhood: Prekindergarten-Grade 3
What is the passing score for STR?
The passing score for the STR is 240.
How much does the STR exam cost?
The STR exam costs $136.
How long does it take to get STR results?
Receiving your STR results depends on the day you took the exam; however, total scores are received within 28 days, and become available at 10 p.m. Central time.
What is the PPR exam?
The PPR exam stands for Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities. The PPR is an exam by the Texas Examinations of Educator Standards (TExES) that measures the understanding of educational theory and pedagogy, and is taken by people who want to teach in the public or private schools within Texas.
Watch the informational video
What is core subjects with STR?
Core subjects with STR are the two State Board for Educator Certification (SBEC) approved educational standards that teachers who teach students in grades PK-6 must demonstrate an understanding of through passing the Core Subjects and also the Science of Teaching Reading exam.
Is the science of teaching reading hard?
The Science of Teaching Reading exam is a 5-hour long test that includes 90 selected-response questions and 1 constructed-response question. The teacher STR exam is extremely challenging and requires a deep understanding of the content specifications.
Is the science of teaching reading hard?
The Science of Teaching Reading exam is a 5-hour long test that includes 90 selected-response questions and 1 constructed-response question. The teacher STR exam is extremely challenging and requires a deep understanding of the content specifications.
What is the science of teaching reading?
The science of teaching reading is based upon educational research conducted that demonstrates the most effective way to teach reading to students from prekindergarten through 6th grade.
Can you retake the STR exam?
Yes, candidates who do not pass the STR exam can retake the test.
How is the STR exam taken?
The STR exam is taken using a computer-administered test (CAT) at a Pearson testing center.
If I don’t pass the STR exam, can I retake only the domains that I didn’t pass?
No, the STR exam is not administered by subtests. If a candidate does not pass the STR test, they must retake the entire test.
If I don’t pass the STR exam, when am I eligible to retake the test?
The current retake policy states that candidates must wait 30 days before they can retake the exam.
How do I prepare for the STR exam?
The best way to prepare for the STR exam is by taking the TeacherSTR online course and studying with the TeacherSTR study guide.
OVERVIEW AND EXAM FRAMEWORK
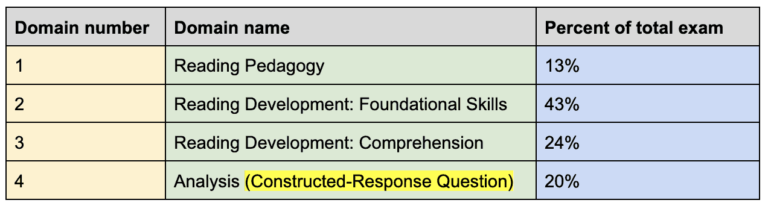
What are the 4 domains in the STR exam and how much is each domain worth?
How many questions are on the science of teaching reading exam?
There are a total of 90 selected-response questions (multiple-choice questions), and 1 constructed-response question (essay question).
What are the competencies of the science of teaching reading?
Each competency includes two major parts:
Competency statement: The knowledge and skills that an entry-level educator in Texas public schools needs to know and be able to do.
Descriptive statements: The set of knowledge and skills eligible for testing.
Domain I—Reading Pedagogy
Competency 001—(Foundations of the Science of Teaching Reading): Understand foundational concepts, principles, and best practices related to the science of teaching reading.
Competency 002—(Foundations of Reading Assessment): Understand foundational concepts, principles, and best practices related to reading assessment.
Domain I—Reading Pedagogy
Competency 003—(Oral Language Foundations of Reading Development): Understand foundational concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of oral language, including second-language acquisition, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level oral language skills.
Competency 004—(Phonological and Phonemic Awareness): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of phonological and phonemic awareness, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level phonological and phonemic awareness skills.
Competency 005—(Print Concepts and Alphabet Knowledge): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of print concepts and alphabet knowledge, including understanding of the alphabetic principle, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level print concepts and alphabet knowledge and their understanding of the alphabetic principle.
Competency 006—(Phonics and Other Word Identification Skills): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of phonics and other word identification skills, including related spelling skills, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level phonics and other word identification skills and related spelling skills.
Competency 007—(Syllabication and Morphemic Analysis Skills): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of syllabication and morphemic analysis skills, including related spelling skills, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level syllabication and morphemic analysis skills and related spelling skills.
Competency 008—(Reading Fluency): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of reading fluency, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level reading fluency.
Domain III—Reading Development: Comprehension
Competency 009—(Vocabulary Development): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to vocabulary development, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level vocabulary knowledge and skills.
Competency 010—(Comprehension Development): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the development of reading comprehension, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of reading comprehension strategies in order to gain, clarify, and deepen understanding of appropriately complex texts.
Competency 011—(Comprehension of Literary Texts): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the comprehension of and critical thinking about literary texts, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade level comprehension and analysis skills for literary texts.
Competency 012—(Comprehension of Informational Texts): Understand concepts, principles, and best practices related to the comprehension of and critical thinking about informational texts, and demonstrate knowledge of developmentally appropriate, research- and evidence-based assessment and instructional practices to promote all students’ development of grade-level comprehension and analysis skills for informational texts.
Domain IV—Analysis (Constructed-Response Question)
Competency 013—(Analysis and Response): Analyze assessment data related to reading development in foundational reading skills and reading comprehension, and prepare an organized, developed written response based on the data and information presented.
CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE QUESTIONS ON THE STR EXAM
How many scorers read each test?
Two people independently read and score each candidate’s STR test. If the two scores differ or are not aligned, additional scoring is conducted.
Can I request a rescore?
Yes, you can request a review for the written-response section. For the selected-response section of the STR test, no score recount can be accounted for.
Does spelling and grammar count on the constructed-response question?
Spelling and grammar do not count toward the open-ended question, unless there are significant errors.
Can I complete the constructed-response question before the selected-response questions?
Yes, you can navigate through the exam freely and can complete the questions in the best possible order for you.
ABOUT HOW THE STR EXAM WAS DEVELOPED
How was the STR exam developed?
The STR exam was developed through the following process:
- Develop exam frameworks
- Through the TExES test committee, test specialists created the STR exam framework based on the Educator Standards that measure the competency of reading standards of teachers.
- Conduct Job Analysis and Validate through Surveys
- Texas educators are surveyed to better understand the importance of each content specification outlined in the exam framework.
- Develop and Review Exam Questions
- Professional exam writers from Texas draft test questions that are designed to measure each domain and competency planned for in the exam framework. Questions are then submitted and reviewed by test experts in Texas to ensure test validity and accuracy.
- Develop and Review Exam Forms
- Once the exam is completed, the test is given to a sample of educators to check that all the questions are fair and equitable.
- Set Passing Standard
- Committee members in Texas meet to set the passing score for the exam, and the Commissioner makes the final decision.
Why is the science of teaching reading important?
The science of teaching reading plays a critical role in the future of education. Teachers must understand the cognitive process of learning and be able to utilize modern day instructional strategies to help students learn deeply.


